When we talk about cybersecurity and particularly identity and access management, we frequently default to thinking about the human element of the risks involved, rather than the machine. But enterprises manage a proliferating number of machines, the rate accelerating with the adoption of cloud, container and microservices technologies—all of which have their own identities, validated by certificates, which present another attack surface to cybercriminals and a considerable management overhead. In this blog post I explore the business case for automating the management of these certificates to reduce work and risk.
Georgia State University's Evidence-Based Cybersecurity Research Group (EBCS) and the University of Surrey have discovered a thriving marketplace for SSL and TLS certificates on the dark web where the certificates are packaged with additional cybercrime services to make it easy to acquire extended validation certificates and perform attacks on web applications to steal data or eavesdrop on encrypted traffic.
A Forrester report, Securing the Enterprise with Machine Identity Protection, identified that organizations do recognize machine identity protection is core to their cybersecurity strategy and that they use three key success measures:
- Faster detection of breaches
- Improving automated compliance with security regulations and policies
- Reducing the total number of breaches
61% say biggest concern..is internal data theft"
The report goes on to state:
“Sixty-one percent of companies say their biggest concern about machine identity and access management failure is internal data theft or loss, followed closely by theft or loss of customer data. At a time when safeguarding data helps generate and protect competitive advantages, it’s imperative that firms invest in the tools that deliver comprehensive machine identity protection.”
But how do individuals in Infosec roles justify the people and software investments required to ensure these risks associated with machine identities are properly mitigated?
The obvious place to start is with the worst-case scenario—the breach. The Breach Level Index tells us that nearly six and a half million data records are lost or stolen every day—that’s 75 a second. And these are numbers that are increasing all the time.
According to the 2017 Cost of Data Breach Study from the Ponemon Institute, sponsored by IBM, puts the global average cost at $3.8 million, or $148 per data record. Again, these numbers are only expected to increase. Fixing a data breach is expensive, fixing it badly can be catastrophic when it comes to reputational damage.
The famous 2018 breach, at Equifax, went undetected for 76 days because of an expired certificate.
So, there’s your first calculation: Avoidance of $3.8M cost of breach
Certificate expiration can cost organizations real money in lots of different ways too though. How about how Ericsson left millions of their UK customers without their mobile network services? Or, the horror, not being able to access Pokémon Go? Or being the party in power in the UK and having your website down? Or not being able to connect on LinkedIn?
All of these examples of the consequences of certificate expiration are downright embarrassing and some more than just inconvenient for the user—some have potential to cost users business and money too.
But what does it cost to do our best to avoid having our machine identities used in a breach in the first place?
From a people perspective we need to reduce the pressure for machine identity security skills and the need for human compliance to focus on machine identity use and management; in other words, we need to automate this activity. Automation reduces errors and mistakes around forgetting to perform activities. We also need to make machine identity management more visible and easier for everyone to understand. In the DevSecOps world there is the tenet that security is not one person or team’s job, but everyone’s job.
From a process point of view, we need to enforce policies efficiently and build an inventory of machine identities. From a human perspective, this could be done by getting the right people in the right meetings (project and sprint planning for example) at the right time—a notoriously hard thing to do, particularly when most organizations experience security skills as a constraint, incidents happen and people want to spend less time meeting and more time doing anyway. Building an inventory of machine identities can be an onerous and time-consuming job that’s almost impossible to maintain manually, especially with the movement to treat machines like cattle, not pets, a challenge once more exacerbated to rapid environment provisioning in the cloud.
Your next calculation: The cost of policy enforcement and inventory creation and management
From a technical perspective, we want to minimize the manual overhead around the switching of certificate authorities and replacement of vulnerable machine identities and be assured that we are responding quickly to cryptographic security events.
Your next calculation: The cost of certificate provisioning and management, and fixing certificate expiration issues
What is the human cost to achieve the level of risk mitigation an automation solution provides?
I’ve put together a table that you might want to use to estimate the costs in your organization, adjusting the amounts for the set-up in your own organization. The calculations are based on managing 1000 machine identities and assuming fully loaded cost of an FTE of $100 per hour (use the calculation: ((a x b) x $100) = c for all lines):
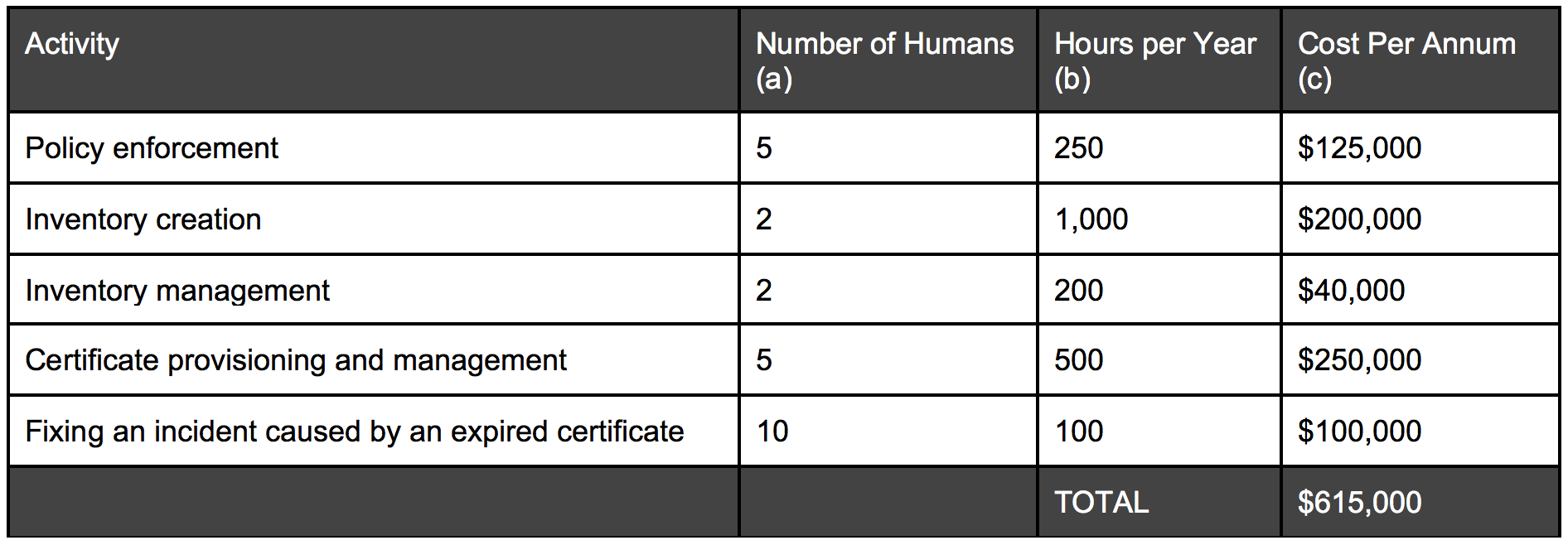
Over and above all of this, you may want to consider the hidden costs of certificate management, things like: slowing down revenue generating functions, fixing avoidable audit findings and stealing resources from more value-added work.
Using your business case, you can justify making an investment in a continuous visibility capability that is actively surveilling machine identities. You’ll be prepared to rapidly identify unauthorized access and privilege escalation and prevent a horrible breach, thus protecting your reputation from damage and avoiding all the necessary remediation costs.
Having comprehensive intelligence across the entire machine identity life cycle that includes certificate enrollment, installation, renewal, and revocation to manage and protect authorized, encrypted communications between machines. This level of machine identity intelligence will allow you to avoid much of the cost associated with managing the certificates in your machine landscape—and be confident you’re covered with your boss, your peers and your auditors.
It’s a safer, cheaper way to run your business and should be a core part of your cybersecurity strategy and operation.
Find out why you need machine identity management
Related posts

2024 Machine Identity Management Summit
Help us forge a new era of cybersecurity
Looking to vulcanize your security with an identity-first strategy? Register today and save up to $100 with exclusive deals. But hurry, this sale won't last!
