Over the past years there has been intensifying interest in robotics and automation. The potential for these technologies to reduce costs and jobs has been highlighted. Deloitte’s research has demonstrated that, while technology contributed to the loss of 800,000 jobs between 2001 and 2015, in the same period it helped create 3.5m new jobs which, on average, were higher skilled and higher paid. The job landscape in the future will be dramatically different. In parallel with moving to greater use of robotics and automation, businesses need to reimagine the shape and role of their human workforce.
The Robots Are Ready. Are You?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), often referred to as ‘robotics’ or ‘robots’, is defined as the software automation of rules-based processes that utilizes the user interface and which can run on any software, including web-based applications, ERP systems and mainframe systems. Therefore, RPA is a computer-coded software, that replaces humans performing repetitive rules-based tasks.
RPA solutions have existed for over a decade, but with recent advancements in technology, they have seen wider deployment in businesses today and have been encouraged by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) as a potential solution to redirect limited resources to accomplish mission outcomes that matter most to citizens.
Deloitte invited organizations globally to take part in an online survey on their use of RPA. The key findings of this survey are included in the report “The robots are ready. Are you?”. According to the survey, continuous improvement and automation remain top of the strategic agenda for many enterprises: 53% of the respondents have already embarked on the RPA journey and a further 19% of respondents plan to adopt RPA in the next two years. If adoption continues at its current level, RPA will have achieved near-universal adoption within the next five years.
RPA is increasingly becoming an enterprise-level opportunity: for 64% of respondents RPA is a strategic or enterprise-wide initiative. This figure has grown significantly over the past year since many organizations that started with function-specific RPA initiatives have grown or consolidated these to take advantage of the broader opportunity across the business.
Take Control of Your Machine Identities With Automation and ELIMINATE Outages!
There is an expectation that robots could deliver a significant portion of current transactional activities. This can enable the human workforce to be redeployed to more value adding activities. RPA implementation has an attractive payback period—just under 12 months. As such, organizations are investing in RPA. Among those that have already implemented RPA, 78% expect to significantly increase investment in RPA over the next three years, with those that are piloting RPA planning to spend an average of $1.5m on RPA. Organizations that have implemented or scaled across the enterprise have already invested an average of $3.5m in robotics.
RPA continues to outperform expectations on non-financial benefits such as accuracy, timelines, flexibility and improved compliance, with at least 85% of respondents reporting that RPA met or exceeded their expectations in these areas. In addition, a total of 61% reported their expectations of cost reduction being met or exceeded.
Securing Bot Certificates for Federal Agencies
One of the top challenges for the enterprises that have implemented, and scaled RPA is building a strong foundation. “The IT organization is essential in setting up a scalable and secure bot infrastructure” says the Deloitte report.
Given the on-going adoption of RPA, securing bots and paying close attention to how they are access systems and data is critical. Existing identity management tools and related security control configurations, such as the implementation of TLS authentication or other multi-factor authentication mechanisms, have proven effective in securing Federal IT systems. Using these technologies, organizations can facilitate secure, auditable access for human and digital users alike.
RPA, A New Attack Surface
The adoption of RPA technology introduces a new attack surface for both human and non-human identities, opening the enterprise to the damaging effects of a data breach. If the accounts and credentials leveraged by both RPA admins and this new digital workforce are left unsecured, an attacker can steal them and gain access to your most critical systems, applications and data. Poor bot identity management can result in key risks not only to Federal agencies but to all companies embracing the potentials of RPA. These risks are visualized in the following diagram, courtesy of Deloitte.
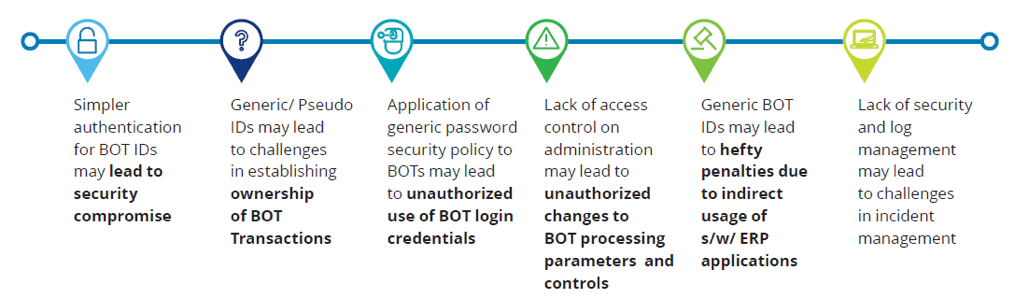
Figure 1: Key Risks to Bot Identity Management
While many RPA solutions may have organic credential managers allowing bots to login to applications, these credentials generally include traditional ‘knowledge-based’ features that leverage usernames and passwords. These credentials are not strong enough to access Federal applications or information that require higher authentication assurance and contain sensitive data in accordance with the FIPS 199 categorization. To accomplish this, machine identities must be issued to enable bot credentialing, authentication and access in accordance with established Federal certificate issuance procedures.
One key consideration to consider when issuing bot certificates is that they should contain information that easily identify Non-Person Entities (NPEs) when they attempt to gain access to applications. In fact, OMB Memorandum M-19-17, titled Enabling Mission Delivery through Improved Identity, Credential, and Access Management, compels agencies to ensure the “digital identity is distinguishable, auditable, and consistently managed across the agency”, to include “establishing mechanisms to bind, update, revoke, and destroy credentials for the device or automated technology.” Additionally, human sponsor correlation is required prior to certificate generation to align accountability with potential system misuse. While these two factors are critical in credentialing bots, other significant requirements also deserve careful consideration.

Figure 2: Bot Credentialing Considerations. Source: Deloitte
These requirements can be broken into several categories: Policy/Governance, Technical Considerations and Procedural Considerations. All considerations are critical; however, the governance input is the catalyst that provides the necessary guidance for the technical and procedural implementers, allowing a secure and compliant solution to operationalize bot credentialing
If you want to learn more on how you can secure your bot credentials, contact the experts at Venafi.
Get a 30 Day Free Trial of TLS Protect Cloud, Automated Certificate Management.
Related posts
