What is an X.509 certificate?
SSL/TLS X.509 certificates are digital files that are used for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS). An SSL/TLS certificate is one of the most popular types of X.509 certificates or a type of public-key certificate which uses the X.509 standard. X.509 certificates contain a public key and the identity of a hostname, organization, or individual.
Initially, the certificate aids in confirming and authenticating the identity of a host or website. It contains details validating the authenticity of the identity information of a host or website. Therefore, by clicking on the displayed padlock or examining the trust mark, the details of the certificate chain tell the origin of the certificate's issuance.The
Additionally, it enables the encryption of data transmitted through a website. By encrypting the data while it's in transit, any sensitive information shared through the website is safeguarded from interception and decoding by anyone aside from the designated recipient.
The credibility of an SSL/TLS certificate is significantly enhanced when it's granted by a reputable Certificate Authority (CA). Such authorities are bound by stringent regulations and guidelines regarding the eligibility for receiving an SSL Certificate. Consequently, possessing a valid SSL Certificate from a recognized CA elevates the level of trust. The endorsement of a certificate by a Certificate Authority (CA), or its validation by another certified body, empowers the certificate holder to utilize the public key for setting up secure connections with another entity or to authenticate documents that have been digitally signed with the matching private key.
Some X.509 SSL/TLS certificates are self-signed, and these certificates will not be trusted for public-facing applications. Because of this, they are mainly used to encrypt and authenticate data within an organization’s network.
SSL/TLS certificates are X.509 certificates with Extended Key Usage: Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1). The "Extended Key Usage" extension lists the "roles" for the entity that uses the certificate. In other words, an entity must use SSL/TLS certificates only for server authentication and nothing else. Otherwise, that entity risks violating the issuing CA's policies.
There are also other common types of X.509 certificates, like Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) and Code Signing (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.3). These files form the basis of encryption and authentication schemes.

TLS Machine Identity Management for Dummies
How do X.509 certificates work?
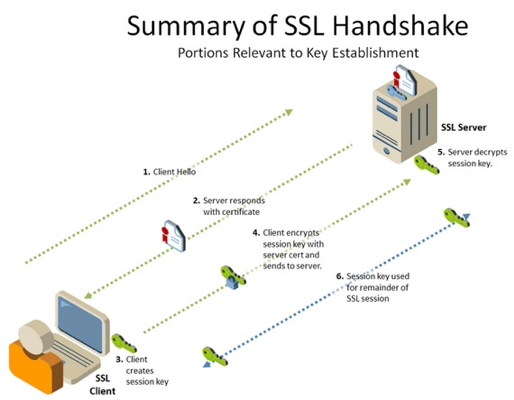
As SSL/TLS certificates enable encryption, they are integral to HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure(HTTPS), a protocol that encrypts all communication exchanged between a website and your browser.
- HTTPS begins once a browser seeks out a webpage that requires security
- The response from the web server includes its public key alongside its digital certificate.
- Next, the browser verifies this certificate is signed by a Certificate Authority (CA).
- Upon successful verification, the browser employs the server's public key to cloak a randomly chosen symmetric encryption key, bundling it with the URL and additional HTTP data, all in encrypted form, and forwards it to the server.
- Provided the public key passes the authenticity check, the server then uses its private key to decrypt symmetric encryption key, the URL, and the HTTP data, followed by dispatching the HTML content and HTTP data, both now secured using the symmetric key.
- Lastly, this symmetric key grants the browser the ability to decrypt the HTTP data, making it visible to the user.
How do I check a site for a valid secure connection?
A typical website lacking SSL/TLS protection will show "HTTP" at the start of its URL in the browser's address bar, signifying "Hypertext Transfer Protocol," the traditional method for sending data across the Internet. Conversely, a website safeguarded by an SSL Certificate will prefix its address with "HTTPS," indicating "Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure."
Every browser has a slightly different way of displaying secure connections. But for all of them, you can check that a website you're visiting is using HTTPS by looking for "HTTPS" in the address bar.
Certain browsers might also showcase a padlock icon adjacent to the web address. Clicking on this icon will typically reveal the name of the entity holding the SSL/TLS certificate. This icon changes to green if an Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificate is recognized by your browser. Should there be a mismatch in the information or if the certificate is out of date, the browser will present a warning or an error notification. Moreover, it has become common for browsers to label all HTTP sites as not secure.
If the certificate has expired, the web browser will display an error message or warning. These alerts could lead a visitor to navigate away from a website. To prevent this from happening, organizations that own websites and use HTTPS need to manage their certificates and make sure the ones they want to keep don't expire.
Managing X.509 certificates
Digital transformation is revolutionizing our connected world, leading to an exponential increase in the number of machines requiring X.509 certificates for secure communication. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has unveiled a comprehensive 400-page manual on how to manage these certificates efficiently. We have summarized this guidance into an ebook for easy understanding. Secure your organization’s certificates by downloading this ebook today.
Automate and Secure Your X.509 Certificates with Venafi TLS Protect
As the digital landscape evolves, the surge in machines needing X.509 certificates for secure interactions has made their management more critical than ever. Recognizing this, Venafi TLS Protect steps in to offer an unparalleled solution, blending the power of automation with cutting-edge security. By automating the lifecycle management of X.509 certificates, Venafi TLS Protect not only simplifies the complex process but also ensures your network remains secure against emerging threats. Don't let the management of X.509 certificates become a bottleneck in your organization's security posture. Embrace the efficiency and reliability of Venafi TLS Protect. Start transforming your certificate management process today and safeguard your digital assets with confidence.
